When manufacturers, engineers, and certification managers search for information about ISO 17025, they are usually trying to answer one practical question: Can I trust this laboratory’s results for regulatory approval and technical decision-making?
ISO 17025, formally published by the International Organization for Standardization in cooperation with the International Electrotechnical Commission, is the globally recognized standard that defines how testing and calibration laboratories must operate in order to produce accurate, impartial, and technically valid results.
Unlike general quality standards, ISO 17025 focuses specifically on laboratories and measurements. It governs how people are trained, how equipment is calibrated, how methods are validated, how uncertainty is calculated, how data are protected, and how results are reported. Together, these requirements form a unified technical framework designed to ensure that every value appearing in a laboratory report can withstand regulatory scrutiny.
The Purpose and Scope of ISO 17025
ISO 17025 applies to testing laboratories, calibration laboratories, and laboratories that perform sampling associated with testing or calibration. Its scope extends across the entire lifecycle of laboratory work, from the moment a customer submits a test item to the issuance of the final report.
The standard establishes requirements in areas such as organizational impartiality, personnel competence, equipment management, environmental control, test methods, measurement uncertainty, recordkeeping, and continuous improvement. This breadth is intentional: reliable results cannot exist without both strong technical controls and disciplined management processes working together.
Impartiality and Confidentiality in ISO 17025
A defining feature of ISO 17025 accreditation is its emphasis on trust. Laboratories must be able to demonstrate that their technical decisions are free from commercial, financial, or organizational pressure. The standard requires formal identification of risks to impartiality and documented actions to mitigate those risks.
Confidentiality is treated with the same seriousness. Laboratories routinely handle proprietary designs, firmware, test data, and early-stage prototypes. ISO 17025 obliges them to establish controls governing access to customer information, physical security of samples, and protection of digital records.
Personnel Competence Under ISO 17025
ISO 17025 recognizes that laboratory quality ultimately depends on people. Even the most advanced instruments cannot compensate for inadequate technical judgment or incomplete training.
Laboratories must define competence requirements for every role that affects test or calibration results and maintain objective evidence that personnel meet those requirements through education, experience, witnessed testing, and technical evaluations.
Equipment Control, Calibration, and Traceability
Instrumentation sits at the heart of any laboratory, and ISO 17025 devotes extensive attention to how equipment is selected, maintained, and calibrated.
Calibration results must be traceable to national or international measurement standards and include known uncertainties, creating an unbroken traceability chain linking results back to fundamental physical units.
In fields such as EMC testing and RF compliance, this discipline is essential for regulatory acceptance.
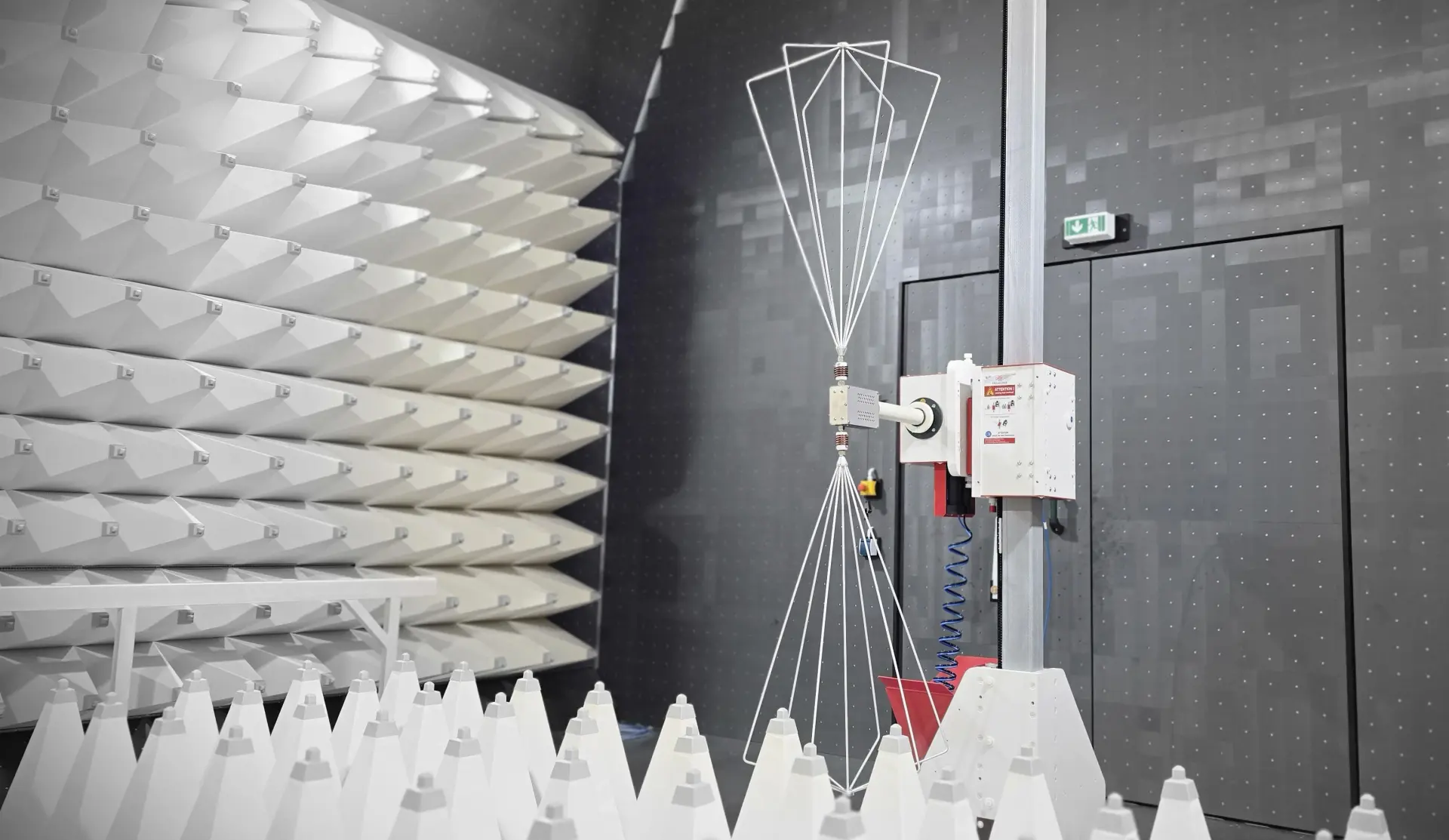
Facilities and Environmental Conditions in ISO 17025
ISO 17025 requires laboratories to define acceptable environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, vibration, electromagnetic background noise, and power quality.
In specialized environments such as shielded rooms and anechoic chambers used for automotive EMC testing, controls extend to absorber performance and ambient noise levels.
Test Methods, Verification, and Validation in ISO 17025
Laboratories are expected to use internationally recognized standards whenever possible and to verify that they can correctly perform those methods before offering them commercially.
Non-standard or internally developed methods require formal validation to demonstrate fitness for purpose and reproducibility.
Measurement Uncertainty in ISO 17025
Every quantitative result carries uncertainty. ISO 17025 requires laboratories to quantify this doubt through structured uncertainty evaluations.
This becomes especially critical in regulatory submissions where margins to limits determine pass or fail decisions.
Reporting and Data Integrity in ISO 17025
ISO 17025 requires that all technical records be complete, secure, and reconstructable, including raw data, calibration certificates, calculations, and deviations.
Reports must clearly describe results, applied standards, environmental conditions, uncertainty where applicable, and accreditation claims.
Why ISO 17025 Matters to Manufacturers
For organizations pursuing certification or regulatory approval, ISO 17025 reduces technical risk, prevents rejected submissions, and supports globally defensible compliance programs.
Final Thoughts
ISO 17025 is far more than a checklist. It is a complete framework governing people, equipment, environments, methods, uncertainty, reporting, and continual improvement.
Selecting an ISO 17025 accredited laboratory is therefore a strategic decision that can directly influence development schedules, certification outcomes, and long-term product confidence.
Related Articles
Stancer Testing-Lab specializes in validating Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) test sites, ensuring your Open Area Test
EMC Testing At Stancer Testing-Lab, we offer comprehensive EMC testing services to enhance product performance
At Stancer Testing-Lab, our system testing services go beyond verifying individual parts, we ensure your
Our world-class testing and certification services ensure your products surpass the most rigorous international standards